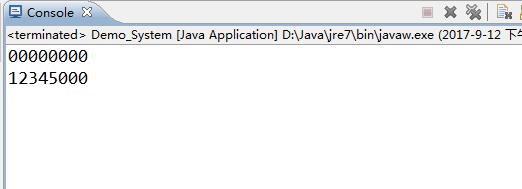
结果示意图:
-
A:System类的概述
- * System 类包含一些有用的类字段和方法。它不能被实例化。
-
* B:成员方法
- * public static void gc()
- * public static void exit(int status)
- * public static long currentTimeMillis()
- * pubiic static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length)
-
* C:案例演示
案例代码
package com.fenxiangbe.regex;
public class Demo_System {
/**
* * A:System类的概述
* System 类包含一些有用的类字段和方法。它不能被实例化。
* B:成员方法
* public static void gc()
* public static void exit(int status)
* public static long currentTimeMillis()
* pubiic static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length)
* C:案例演示
* System类的成员方法使用
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
//demo1();
//demo2();
//demo3();
int[] arr1 = {1,2,3,4,5};//数组的静态初始化
int[] arr2 = new int[8];//数组的动态初始化
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {//复制之前arr2的值
System.out.print(arr2[i]);
}
System.out.println();
//把arr1的数组值复制到arr2
System.arraycopy(arr1, 0, arr2, 0, 5);//arr1表示被复制的数组,第一个0表示被复制的数组是从0索引开始复制,arr2表示复制到目标数组,第二个0表示复制目标数组是从0索引开始替换,5表示被复制数组的长度
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {//复制之后arr2的值
System.out.print(arr2[i]);
}
}
public static void demo3() {
long l1 = System.currentTimeMillis();//currentTimeMillis()此方法是指获取当前时间的毫秒值
for (int i = 0; i <1000; i++) {
System.out.println("*");
}
long l2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(l2 - l1);//运行之后的时间减去运行之前的时间 就是运行所用的时间
//本案例测试26毫秒,一秒等于1000毫秒,就是执行了一千次*号 只用了26毫秒,
}
public static void demo2() {
System.exit(0);//终止程序运行,非0状态也能终止 ,但是属于异常退出,不建议使用 ,按照惯例选择0
System.out.println("执行这一句……");
}
public static void demo1() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Demo();//产生垃圾
System.gc();//启动垃圾回收器 ,把垃圾清理
}
}
}
class Demo {
public void finalize() {//重新object类中的finalize方法
System.out.println("清理垃圾!!!");
}
}

 吾爱乐享
吾爱乐享









评论前必须登录!
注册